Fraunhofer IZM enables bidirectional charging with onboard charger
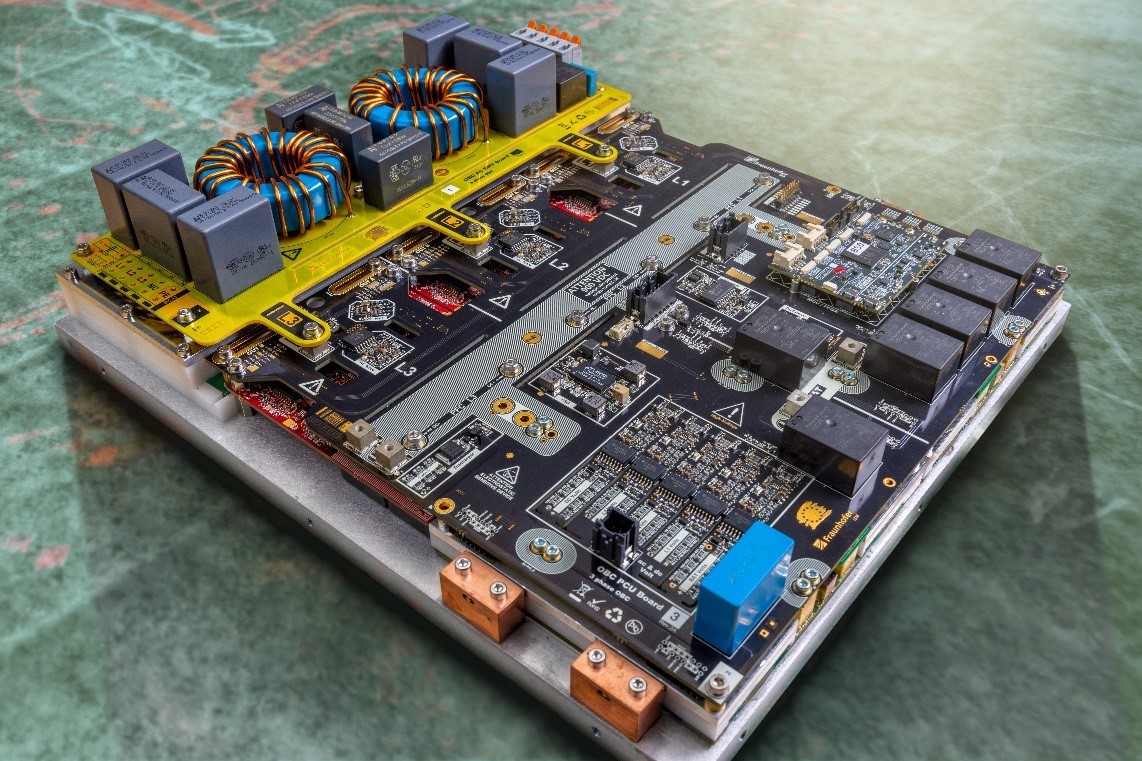
The Fraunhofer IZM has tackled the issue of an onboard charger that can be used with AC at home to charge rapidly. The German research institute developed an onboard charger that reduces the volume of such devices to three litres, halving the volume compared to conventional chargers, but doubling the charging power from 11 to 22 kW.
The module is compatible with 400 and 800-volt batteries and has an efficiency of over 97 per cent. The new charging technology can not only charge the car’s battery with grid or home power but the use the car’s battery to contribute in the other direction (hence the term, bidirectional charging) to the home and/or grid with bi-directional charging called vehicle-to-grid (V2G).
To pave the way for this new onboard charger, several components were developed at Fraunhofer IZM and combined in a small space. One of these components is a sine-amplitude converter (SAC) – a resonant high-frequency transformer that initially ensures galvanic isolation of the vehicle battery from the supply grid. However, the actual progress of the SAC is made possible by the gallium nitride semiconductors (GaN) used – novel and powerful semiconductors with a wide bandgap, better known as wide-bandgap semiconductors. They make it possible to switch the transformer on and off at a clock frequency of 1.3 MHz, i.e. 1.3 million times per second. Oleg Zeiter from Fraunhofer IZM, who played a leading role in the development of the OBC, explains: „These high frequencies mean that we can totally rethink how we design the module.“
Another central component in an OBC is the so-called power factor correction converter (PFC). It forms the interface to the supply network and stabilizes the AC voltage on the input side in sinusoidal form at – depending on the network – 50 or 60 Hz. This requires chokes – a very bulky component in previous onboard chargers, which is also very expensive to manufacture.
Fraunhofer IZM has now developed a flat PFC choke based on a printed circuit board, with four magnetically coupled windings on a common ferrite core. This has the great advantage of cost-effective machine production and saves a lot of space. Although the planar design with PCB only allows lower inductances, these are no obstacle for the PFC, which is built with SiC switches and clocked at 140 kHz. „Because we only ever switch on the current for an extremely brief moment in time, it never reaches high amperage, even at low inductivity – all thanks to the quick switching,“ says Oleg Zeiter.
Thanks to these assembly and connection techniques, Fraunhofer IZM was finally able to develop the new onboard charger. “In principle, we now only need one large circuit board. Thanks to our packaging solutions, everything else only needs to be applied to this PCB by the machine,” says Oleg Zeiter. In this way, manufacturing costs can be significantly reduced.
Anyone interested in seeing the new onboard charger can do so at the Fraunhofer IZM stand (Hall 5, Stand 300) in Nuremberg, Germany from June 11 to 13, 2024. The device will be presented to the public there at PCIM Europe, an international trade fair for power electronics.




0 Comments